球面収差補正装置(Csコレクター)
球面収差補正装置(Csコレクター)
Cs corrector
[目次:レンズ系]
負の球面収差係数を作り出し、磁界軸対称レンズである対物レンズ、コンデンサーレンズの正の球面収差係数を打ち消す装置。1) 極性が反対の2個の六極子とそれらを繋ぐトランスファーレンズから成り、第一の六極子で負の球面収差係数を作り出す。第一の六極子で作られる不用な3回対称のビームの歪みは第二の六極子によって取り除かれる。負の球面収差は第二の六極子によって倍加される。2) 八極子と四極子を組み合わせた素子を3対用意し、第一の素子でX方向に負の球面収差を発生させ、第二の素子でY方向に、第三の素子でそれらの中間方向に負の球面収差を発生させる。対物レンズの球面収差の補正により高いTEM像分解能、コンデンサーレンズの球面収差の補正により、より小さく高強度のプローブが得られ、より高分解能のHAADF像、一原子列からの元素分析ができる。
Cs corrector⇒図 :二段六極子型球面収差補正装置
六極子(または十二極子)内における電子線の軌道(左上)とレンズ配置模式図(右下)
二段六極子型球面収差補正装置では、厚みを持った六極子場が負の球面収差を発生させることを利用して収差補正を行う。左上図は、六(十二)極子内での電子線の軌道を10mradの角度毎に(内側の水色から外側の赤色の線)示したものである。一段目の六極子(Hexapole) 場で負の球面収差が発生する。軌道は本来必要の無い三角形状になってしまうが、二段目の極性が反対の六極子場で一段目の六極子場で生じた三角形状が打ち消されて円筒対称軌道に戻る。二段目の六極子は一段目の六極子と同じ負の球面収差を作り、球面収差量は二倍になる。軌道は、六極子場を励磁しない場合(黄緑色)に比べて、より発散方向(外側)に広がる(赤色)。この負の球面収差を用いて、対物レンズの正の球面収差を打ち消す。なお、右下の図中のトランスファーレンズは、一段目の六極子から出た光線をその形状を保って二段目の六極子に転送するためのもので、左上の図では、その働きは省略してある。
The "Cs corrector" produces a negative spherical aberration coefficient (Cs) to cancel positive Cs of the objective and condenser lenses, which are axially-symmetric magnetic field lenses. The following Cs correctors are now in practical use. 1) One consists of two hexapoles with opposite polarity and transfer lenses that connect the hexapoles. The first hexapole produces a negative Cs. The unnecessary three-fold distortion produced by the first hexapole is compensated by the second hexapole. The value of negative Cs is doubled by the second hexapole. 2) The other consists of three pairs of elements combining octupoles and quadrupoles. Negative Cs is produced in the X direction by the first element, in the Y direction by the second element and the intermediate direction by the third element, respectively. Cs correction of the objective lens achieves a higher resolution TEM image. Cs correction of the condenser lens leads to a smaller, higher-intensity electron probe, thus, enabling us to obtain a higher-resolution HAADF image and to perform elemental analysis of one atomic column.
Figure shows the schematic of a Cs corrector and its basic action. The corrector, which consists of two hexapoles with opposite polarity and transfer lenses connecting the hexapoles, produces a negative Cs and cancels a triangle shape of the beam caused by the first-stage hexapole field using the second-stage hexapole field.
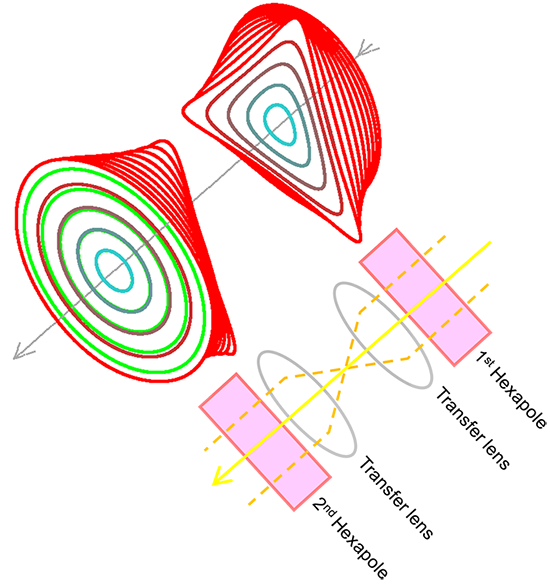
Fig.Two-stage hexapole Cs corrector
Electron trajectory in hexapoles or dodecapoles (upper left) and schematic of lens configuration (lower tight)
In a two-stage hexapole Cs corrector, the thick hexapole field produces a negative Cs, and this action is used to correct the positive Cs of the objective lens. Upper left figure shows the cross section of the electron trajectory in the hexpoles for every 10 mrad angle (from inside blue line to outside red line). The first-stage hexapole field creates a negative Cs but an unwanted triangle shape trajectory. The second-stage hexapole field with the opposite polarity again creates the same amount of negative Cs and the opposite sense of triangle to cancel the triangle shape trajectory caused by the first hexapole, As a result, the amount of negative Cs is doubled and a cylindrical symmetric trajectory is retrieved. Owing to the negative Cs, the cross section of the trajectory expands outwards (shown in red), compared to the trajectory for the case of no hexapole field (in green). With the use of this negative Cs, the positive Cs of the objective lens is canceled. It should be noted that, the transfer lens (lower right figure) is used to transfer an electron beam emerged from the first-stage hexapole into the second-stage hexapole while preserving the beam shape. In the upper left figure, the action of the transfer lens is omitted.
関連用語から探す
説明に「球面収差補正装置(Csコレクター)」が含まれている用語






