結晶構造因子
結晶構造因子
crystal structure factor
[目次:理論(電子の散乱/回折/結像)]
結晶中の1個の単位胞からの回折波(反射波)の振幅と位相を表すもので、単位胞中の原子の種類と位置によって決まる。結晶構造因子から、反射波の相対強度や反射の消滅則が求まる。結晶構造因子Fgは次式のように表現される。
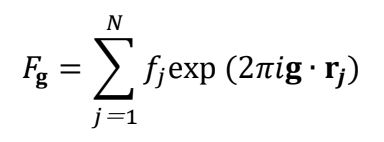
ここで、fjは単位胞中のj番目の原子の原子散乱因子、g は逆格子ベクトル、rj はj番目の原子の座標である。和は、単位胞中の全ての原子にわたって行う。位相項 exp は、回折波が入射波に対してベクトルg だけ方向を変えるときに各原子からの波の位相の違いを表している。入射波 k0 と回折波 k および逆格子ベクトル g の関係を図 1 に示す。
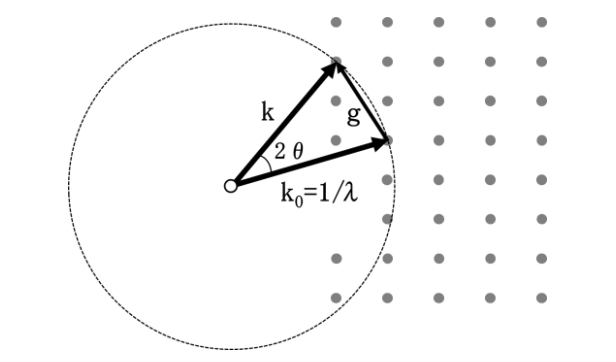
図 1: 入射波 k0と回折波 k および逆格子ベクトルgの関係。k0の大きさは 1/λ(λは波長)である。入射波は結晶によって反射gをおこし、回折波は k ( = k0 + g)の方向に進む。なお、k の長さは見やすさのために短く書いている。200kV の入射電子線に対する k0の長さは逆格子ベクトルgの長さの 50 倍以上になっている。
g は、逆格子の基本ベクトル(a*、b*、c*)と反射の三つの指数(h、k、l)を使って、g= ha*+kb*+lc*と書ける。rjは、単位胞を表す基本ベクトルと原子の位置座標の成分を使って、rj = uja + vjb + wjc と書ける。これらを上のFgの式に代入すると、
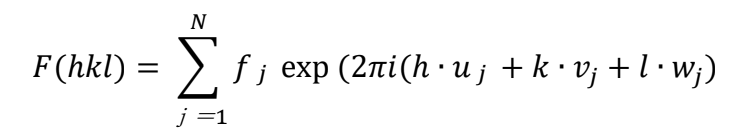
となる。|F(hkl)|2は hkl 反射の相対強度を表す。F(hkl) = 0 になる場合、反射が消滅するという。
例として、体心立方構造の場合の反射強度と消滅則を示す。体心立方構造では単位胞中の原子位置は000 と12 12 12だから、
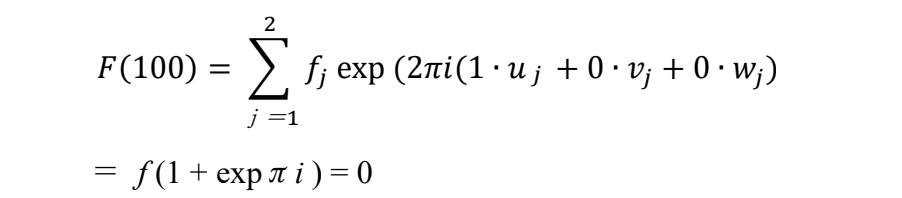
となり、100 反射は消滅する。200 の場合は
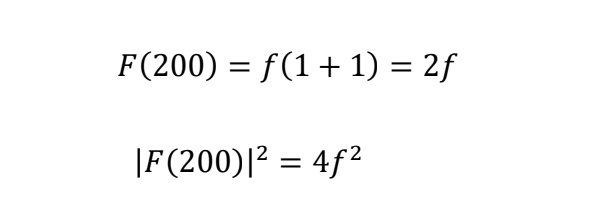
となり、200 反射波の強度は4f 2に比例する。指数の和 h + k + l が偶数のときに回折波は強度を持ち、奇数のときは消滅する(消滅則)。
The crystal structure factor represents the amplitude and phase of a diffracted wave (reflected wave)from a unit cell of a crystal. The factor is given by the atom species and their positions in the unit cell. From the crystal structure factor, the relative intensity of the reflected wave and the extinction rule of the reflections are obtained.The crystal structure factor Fgis expressed as the next equation.
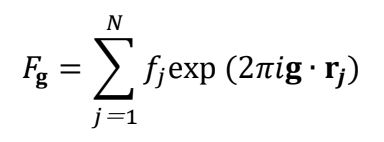
Here, fj is the atomic scattering factor of thej-th atom in a unit cell, g is the reciprocal lattice vector, and rj is the coordinate of the j -th atom. The summation is performed over all the atoms in the unit cell. The phase term exp represents a difference in the phase of the wave from each atom when a diffracted wave changes the direction by the reciprocal lattice vector g with respect to the incident wave. Fig. 1 shows the relation between the incident wave k0, the diffracted wave k and the reciprocal lattice vector g.

Fig. 1. Relation between the incident wave k0, the diffracted wave k and the reciprocal lattice vector g. The magnitude of k0 is 1/λ (λ: wavelength). The incident wave causes a certain reflection g by crystal, then the diffracted wave (reflection beam) travels in the direction of k (= k0+ g). It is noted that in the figure, k is depicted in a short length for convenience: for an incident electron beam of 200 kV, the magnitude of k0 is more than 50 times larger that of the reciprocal lattice vector g.
g can be written as g=ha*+kb*+lc* using the reciprocal lattice vectors and three indices of the reflection. rj can be written as rj = uja + vjb + wjc using the unit cell vectors and the components of positional coordinates of the atoms. Substituting these into the above equation Fg,
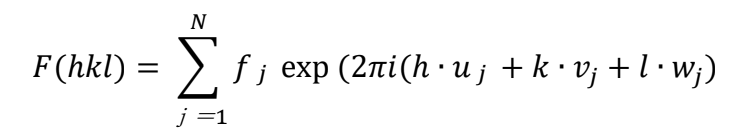
Here, |F(hkl)|2 expresses the relative intensity of the hkl reflection. If F(hkl)=0, the reflection hkl disappears.
As an example, the reflection intensity and extinction rule for the body-centered cubic structure are given. In the body-centered cubic structure, the atomic positions in the unit cell are 000 and 12 12 12.
Then, the following results are obtained.
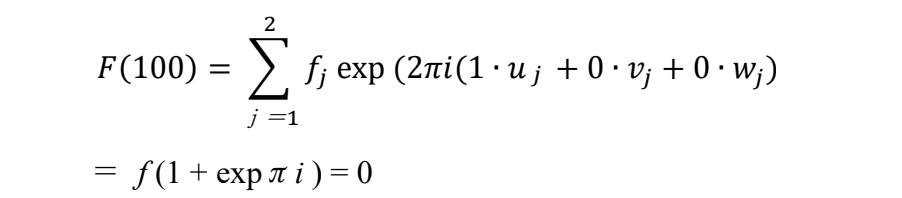
That is, the 100 reflection disappears.
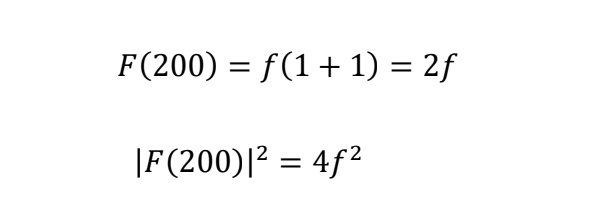
Thus, the intensity of the 200 reflection is proportional to 4f 2. When the sum of the indices h + k + l is an even number, the diffracted wave has intensity, but when the sum is an odd number, the diffracted wave disappears (extinction rule).
関連用語から探す
説明に「結晶構造因子」が含まれている用語






