コンデンサーミニレンズ
コンデンサーミニレンズ
condenser mini lens
[目次:レンズ系]
コンデンサーレンズと対物レンズの間で、観察モードに適した収束角を持つビームを作るレンズ(図1)。
励磁を強くすると平行照射になり、明暗視野像やHREM像の観察仕様の照射になる(図2)。
コンデンサーミニレンズの励磁が弱いときは収束角が大きく、STEM、CBED、分析仕様の照射(微小領域照射)になる(図3)。
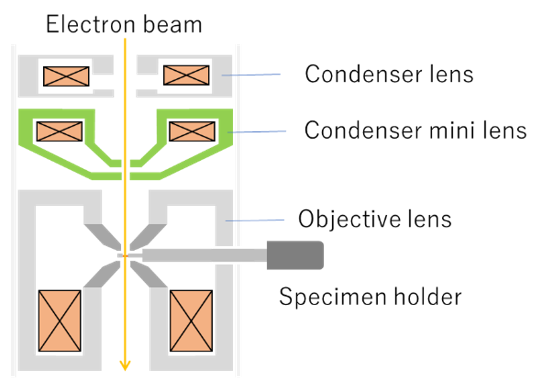
図1 コンデンサーミニレンズ(緑)とその近傍のレンズの配置
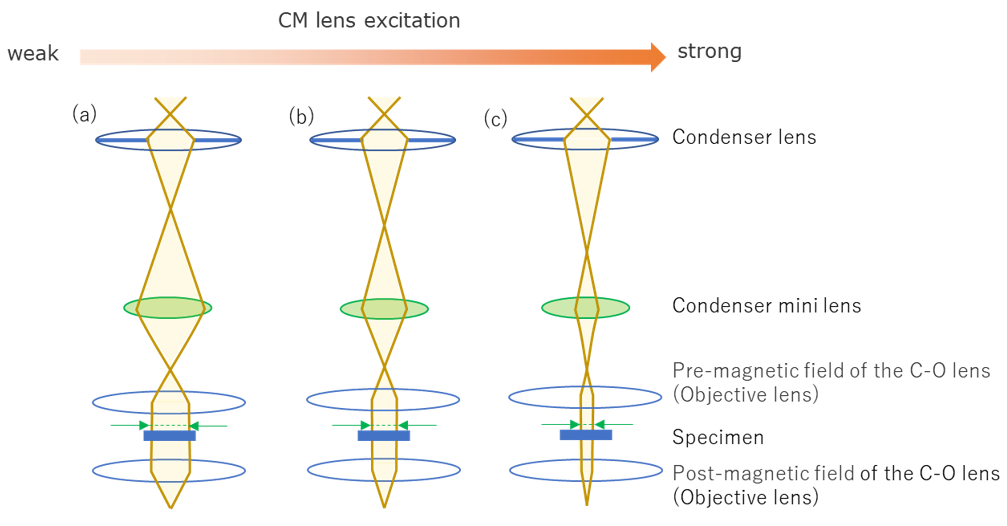
図2 平行照射時のコンデンサーミニレンズの励磁と光線図の関係
試料を平行照射して透過像を観察する際に用いる。
(a) 低倍観察用の光線図。CMレンズの励磁は弱い場合で、広範囲を平行照射することができる。
(b) 中程度倍率の光線図。CMレンズの励磁を強くすることで、より狭い領域を平行照射することができる。
(c) 高倍観察用の光線図。さらにCMレンズの励磁を強くして、さらに狭い領域を平行照射することができる。
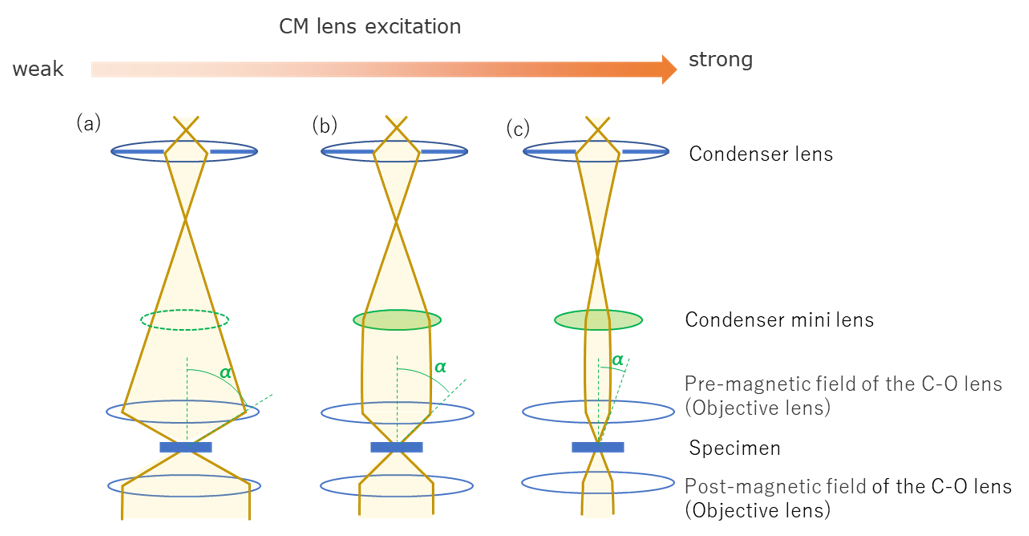
図3 収束照射時のコンデンサーミニレンズの励磁と光線図の関係
試料の微小領域を照射する際に用いる。
(a) STEM像観察用の光線図。CMの励磁をOFFにして、最も微小なプローブを作ることができる。
(b), (c) 収束電子回折用の光線図。CMレンズの励磁を変化させることで収束角(α)を変化させ、回折ディスクの大きさを調整することができる。
The condenser mini lens (CM lens), which is placed between the condenser lens and the objective lens, produces an electron beam with a convergence angle suitable for various observation modes (Fig. 1).
When the excitation of the CM lens is strong, parallel illumination of the electron beam is achieved for observations of bright- and dark-field images and HREM (high resolution electron microscope) images (Fig. 2).
On the other hand, when the lens excitation is weak, convergent illumination (small-area illumination) with a large convergence angle is achieved for observations of STEM (scanning transmission electron microscope) images, CBED (convergent beam electron diffraction) and EELS & EDS analyses (Fig. 3).

Fig. 1 Schematic of the positions of the condenser mini (CM) lens (green) and lenses in the vicinity of the CM lens.

Fig. 2 Ray paths of parallel illumination for the different excitation strengths of the CM lens.
The parallel illumination is used to observe transmission electron microscope (TEM) images.
(a) Ray path for low-magnification image observation. A large specimen area is illuminated by a weak excitation of the CM lens.
(b) Ray path for medium-magnification image observation. A smaller area is illuminated by increasing excitation of the CM lens.
(c) Ray path for high-magnification image observation. A small area is illuminated by a strong excitation of the CM lens.

Fig. 3 Ray paths of convergent illumination for the different excitation strengths of the CM lens.
The convergent illumination is used to form a small electron probe on a specimen.
(a) Ray path for STEM image observation, where a probe as small as possible is required. The CM lens excitation is set in the off state.
(b), (c) Ray paths for CBED pattern observation. The CM lens excitation is varied to change the convergence angle (α) of the electron beam or to adjust the size of the CBED disk.
関連用語から探す
説明に「コンデンサーミニレンズ」が含まれている用語






