GPゾーン
GPゾーン
GP zone
[目次:結晶等(結晶構造/材料試料)]
面状に析出した溶質原子のプレートのことで、A. Guinier(仏)とG.D.Preston(英)が独立に、X線ラウエ斑点上から延びるストリークの解析から発見した面上に析出した溶質原子のプレートのことで、発見者の名前をとりGuinier-Preston(GP) Zoneと呼ばれている。具体的には、AlやMgを主成分としCuなどの溶質原子を含む時効硬化型合金において、過飽和固溶体を急冷し低温で時効処理を行うと、平衡状態図に現れない析出物としてCuなどの溶質原子が母相の{001}面に格子整合して1~2枚の原子面として偏析する。Al, Mg合金等における時効硬化の一因となる。電子顕微鏡の明視野像では、格子歪による線状のコントラストとして観察され、高分解能像では溶質原子の並びが直接観察される。
GP zone ⇒図
GPゾーンを含むAlCu合金の明視野像。加速電圧: 100 kV。
GPゾーン(Cuの析出物)の部分はブラッグ条件から外れており、明視野では明るく(白く)観察されている(白い矢印)。
"GP zone" means a plate that is composed of solute atoms segregated on a plane. The zone was discovered independently by A. Guinier and G. D. Preston through the analysis of streaks extending from X-ray Laue spots. It is named Guinier-Preston (GP) Zone after the two researchers. In the case of an age-hardened alloy that consists of Al or Mg but includes minute solute atoms (Cu, etc.), when its super-saturated solid solution is rapidly cooled and undergoes an aging treatment at a low temperature, solute atoms (Cu, etc.) are precipitated as one or two atomic planes with lattice matching on the {001} plane of the parent phase. It is noted that they do not appear as precipitates in the equilibrium state. The GP zone causes age hardening of alloys containing Al or Mg. In a bright-field image, the GP zone shows a line contrast due to lattice distortions. In a high-resolution image, the arrangement of solute atoms is directly observed.
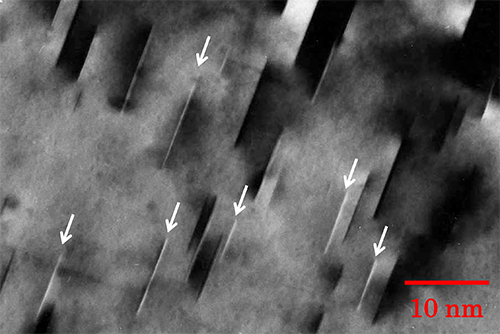
Bright-field image of an AlCu alloy containing GP zones taken at an accelerating voltage of 100 kV.
GP zones (Cu precipitates) are seen to be bright (white) lines, indicated by white allows, because they do not satisfy Bragg condition.
説明に「GPゾーン」が含まれている用語






