デバイワラー因子(温度因子)
デバイワラー因子(温度因子)
Debye-Waller factor
[目次:理論(電子の散乱/回折/結像)]
原子の熱振動 (格子振動) の大きさを表す因子でB因子と言われる。Bは、熱振動による原子の平均二乗振幅を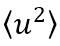 とすると
とすると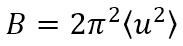 で与えられ、通常Å2で表す。X線、中性子、電子線の原子による散乱振幅の散乱角依存性 (θまたはk依存性) は、次式によって与えられる。
で与えられ、通常Å2で表す。X線、中性子、電子線の原子による散乱振幅の散乱角依存性 (θまたはk依存性) は、次式によって与えられる。
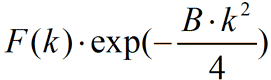
ここで、Fは熱振動のないときの原子散乱振幅であり、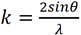 (λ: 量子線の波長、θ:散乱角の1/2) である。B因子によって高散乱角側 (θまたはkが大きい領域) で、散乱 (ブラッグ反射) の振幅が減衰する。試料の温度を下げると、熱振動が小さく抑えられBの値は小さくなる。
(λ: 量子線の波長、θ:散乱角の1/2) である。B因子によって高散乱角側 (θまたはkが大きい領域) で、散乱 (ブラッグ反射) の振幅が減衰する。試料の温度を下げると、熱振動が小さく抑えられBの値は小さくなる。
その結果、高次の反射の振幅の減少が抑えられるため、高次の反射の強度が増し観察しやすくなる。
The Debye-Waller factor expresses the magnitude of thermal vibrations (lattice vibrations) of atoms, called B factor. B is given by 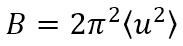 and expressed in units of Å2, where
and expressed in units of Å2, where 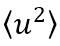 is the mean square amplitude of an atom due to thermal vibration. The angular dependence of scattering amplitude (θ or k dependence) of an atom for X-rays, neutrons and electrons, is given by the following equation.
is the mean square amplitude of an atom due to thermal vibration. The angular dependence of scattering amplitude (θ or k dependence) of an atom for X-rays, neutrons and electrons, is given by the following equation.
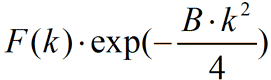
Here, F is the atomic scattering amplitude without thermal vibration, and 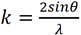 (λ: the wavelength of a quantum wave, θ : half angle of the scattering angle). Due to the B factor, the amplitude of the scattering (Bragg reflection) is attenuated at high scattering angles (at θ or large k). As the temperature of a specimen is lowered, thermal vibrations are reduced and the value of B becomes small. As a result, the decrease in the amplitude of high order reflections is suppressed and the intensities of those reflections are increased, making them easier to observe.
(λ: the wavelength of a quantum wave, θ : half angle of the scattering angle). Due to the B factor, the amplitude of the scattering (Bragg reflection) is attenuated at high scattering angles (at θ or large k). As the temperature of a specimen is lowered, thermal vibrations are reduced and the value of B becomes small. As a result, the decrease in the amplitude of high order reflections is suppressed and the intensities of those reflections are increased, making them easier to observe.
関連用語から探す
説明に「デバイワラー因子(温度因子)」が含まれている用語






