ミラー指数
ミラー指数
Miller index
[目次:結晶等(結晶構造/材料試料)]
結晶の原子面(格子面)を指定する三つの指数h,k,lのこと。原点を通らず原点に一番近い原子面を考えるとき、その原子面が、結晶軸a,b,cと交わる座標をu,v,wとし、結晶の単位胞の長さをa,b,cとすると、ミラー指数は、それらの比a/u, b/v, c/wで与えられる。これらの比が分数になるときは整数化したものを使う。
図1の例では、格子面がa, b, c軸と交わる座標はu=a/4, v=b/1, w=c/2である。a/u = 4, b/v = 1, c/w = 2となるので、ミラー指数はh=4, k=1, l=2となる。すなわち、図示された面は(412)面である。なお、結晶の面を表すときは丸括弧で指数を囲うことになっている。(結晶中で方向を表すときは指数を角括弧[]で囲って区別する。)
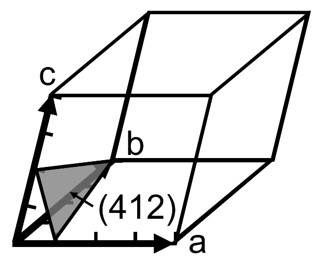
図1:ミラー指数
“Miller index” is a set of three indices h, k, l that identify the atomic plane (lattice plane) of a crystal. When considering the atomic plane closest to the origin without passing through the origin, let u, v and w be the coordinates intersecting the crystal axes a, b and c, and the lengths of the unit cell of the crystal be a, b and c, Miller index of the plane is given by a/u, b/v, c/w. If any of the ratios a/u, b/v, c/w takes a fractional number, the Miller index is expressed by rewritten with integral numbers.
In the example shown in Fig. 1, the coordinates at which the atomic plane intersects the a, b, c axes are u = a/4, v = b/1, w = c/2. Since a/u = 4, b/v = 1, c/w = 2, the Miller index is h=4, k=1, l=2. That is, the lattice plane shown in the figure is the (412) plane. When expressing a plane in a crystal, the index is enclosed in parentheses. (When expressing a direction in a crystal, the index is enclosed in square brackets [ ])

Fig. 1. Miller index.
関連用語から探す
説明に「ミラー指数」が含まれている用語






