ネガティブ染色
ネガティブ染色
negative staining
[目次:試料等(試料および試料作製)]
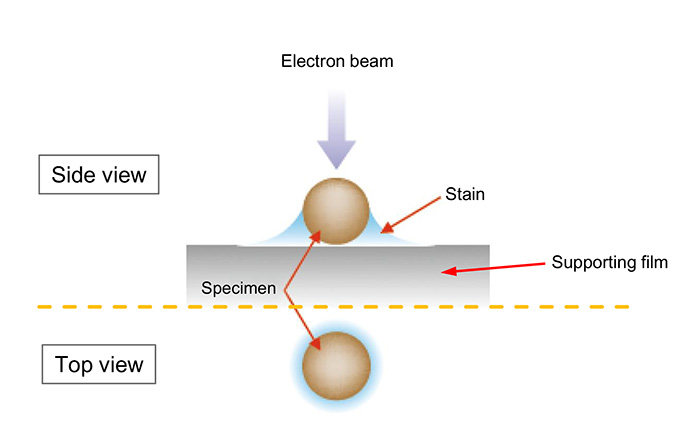
試料の隙間や周辺部の支持膜上に重金属を残留させること。ネガティブ染色によってTEM像のコントラストの増感を行うことができる。
試料となるウイルスや精製したタンパク質等の水溶液を支持膜の上に滴下し、ろ紙で余分な水分を吸い取る。その後、すぐさま酢酸ウランやリンタングステン酸といった重金属を含む染色液を滴下し、ろ紙で水分を吸い取り、乾燥させる。このような操作を行うと、試料の隙間や周辺部の支持膜上に重金属が残り、その部分は電子線を散乱して暗く見えるため、試料の形態が浮き彫りになる。電子染色の一種であるが、試料自身を染めるのではないため "負(ネガティブ)染色" と呼ばれる。
Negative staining is one of electron staining techniques. This technique leaves heavy metals at the gaps in a specimen and on the supporting film at the surrounding regions of the specimen. Negative staining enables enhancement of the TEM image contrast.
An aqueous solution of viruses or purified proteins, etc. is dropped onto a supporting film, and then excessive water is removed from the specimen with a filter paper. Immediately after the removal of excessive water, a staining solution containing heavy metals (uranium acetate, phosphotungstic acid, etc.) is dropped onto the specimen. Then, water is removed from the specimen with a filter paper to dry the specimen, leaving the heavy materials at the gaps and on the supporting film at the surrounding regions of the specimen. As a result, these regions appear dark due to strong scattering of incident electrons, and the morphology of the specimen is elucidated. Since the specimen itself is not stained, this technique is termed "negative" staining.
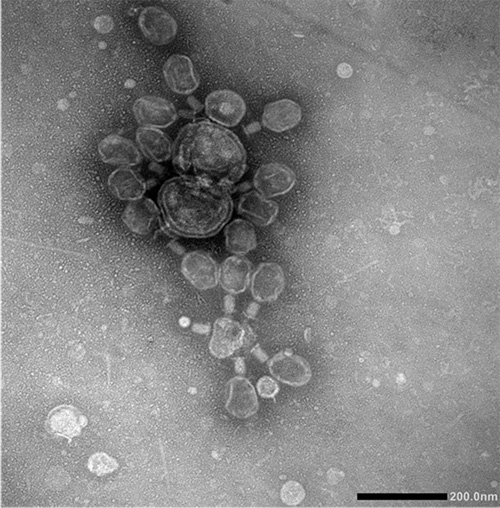
TEM image of negatively stained bacteriophage T4
関連用語から探す
説明に「ネガティブ染色」が含まれている用語






