プリセッション電子回折
プリセッション電子回折
precession electron diffraction
[目次:理論(電子の散乱/回折/結像)]
光軸に対してある角度に傾斜した入射電子線を歳差運動させながら試料に照射し、動力学的効果を軽減させた電子回折図形を取得する方法。
入射電子線を傾斜(最大5°程度)し歳差運動させて試料上のある点に照射させるには、照射系の2段偏向コイルが用いられる。得られる電子回折図形が入射電子線の歳差運動のためにスクリーン面上で移動しないようにするために、試料を通過した電子線を結像系の2段偏向コイルにより光軸上に振り戻す(デスキャン)。
電子線を歳差運動させながら試料に照射すると、同時反射の効果(同時に強く励起された他の反射を経由して、ある反射が強められる効果)が抑えられ、観測される回折強度は運動学理論から期待される回折強度に近づく。
また、電子線の歳差運動により、エワルド球に乗る逆格子点の数が増え、高次の回折点も現れる。このようにして得られた回折強度は、X線回折法で用いられている直接法などの方法を適用して構造解析に用いられる。複雑な構造を持つ無機結晶、有機結晶、ゼオライトなど、微小結晶しか得られない物質の構造解析に利用される。
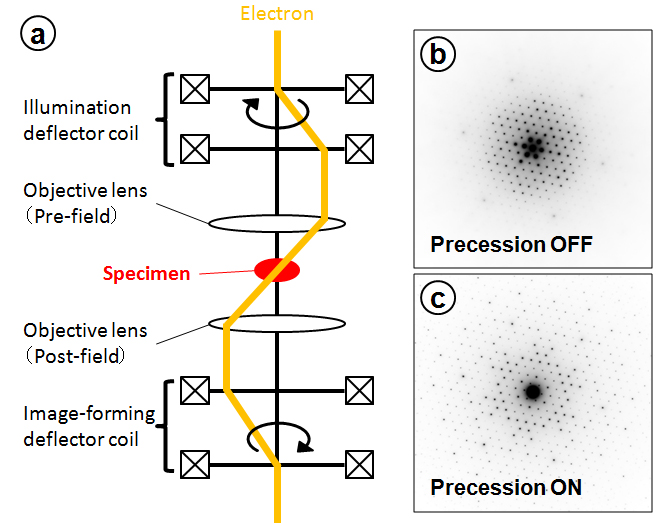
(a) プリセッション電子回折の光線図。照射系の偏向コイルを用いて、入射電子線を試料上で光軸に対してある傾斜角で歳差運動させ、試料を通過した電子線を、結像系の偏向コイルを用いて光軸上に振り戻すことにより、プリセッション電子回折図形を得る。
(b)ガーネット[111]入射による通常の電子回折図形と(c)プリセッション電子回折図形。 図(c) では、電子線を歳差運動させることにより、運動学理論から期待される回折強度に近い回折図形が得られている。また、通常の電子回折図形(b)より、高次の反射が多数現れている。
Precession electron diffraction is an electron diffraction method to obtain an electron diffraction pattern with a less dynamical diffraction effect by precessing the incident electron beam under a certain tilt angle with respect to the optical axis. A two-stage deflector coil in the illumination lens system is used to precess the tilted beam (up to approximately 5°) and to illuminate the beam onto a certain point on a specimen. Then, a two-stage deflector coil (below the specimen) in the image-forming lens system is used to compensate the displacement of the incident electron beam from the optical axis (de-scan), so that the incident beam subjected to the precession stays at the center of the screen. Illumination of such a precessed electron beam suppresses enhancement of the intensity of the reflections due to “double reflection” (an additional excitation via the other strongly-excited reflections). As a result, the observed diffraction intensities become close to those expected from the kinematical diffraction theory. Owing to the precession of the incident electron beam, the number of reciprocal lattice points crossed by the Ewald sphere increases and thus, high-order diffraction spots appear.
The obtained diffraction intensities are utilized for crystal structural analysis by applying the analysis techniques (direct method, etc.) developed for X-ray crystal structure analysis. The electron diffraction method is effectively used for structural analysis of inorganic crystals with complicated structures (e.g. zeolite) and organic crystals, which are often crystallized only with a size up to a micrometer order.

(a) Ray diagram of precession electron diffraction. A precession electron diffraction pattern is obtained by precessing the incident electron beam under a certain tilt angle with respect to the optical axis using a two-stage deflector coil in the illumination lens system, and then by compensating the displacement of the incident electron beam from the optical axis using a two-stage deflector coil in the image-forming lens system.
(b) An ordinary electron diffraction pattern and (c) a precession electron diffraction pattern obtained from garnet at [111] incidence. In Fig. (c), the precession of the incident electron beam enables us to obtain a diffraction pattern that has diffraction intensities being close to those expected from the kinematical diffraction theory. Furthermore, more high-order reflections appear compared with the number of reflections in the ordinary diffraction pattern (b).
関連用語から探す
説明に「プリセッション電子回折」が含まれている用語






