オートラジオグラフィー
オートラジオグラフィー
Autoradiography (Autoradiography in Electron Microscopy)
[目次:理論(電子の散乱/回折/結像)]
生体試料の特定の部位を、放射性同位元素を含む物質で標識し、電顕像でその特定の部位を可視化する方法。
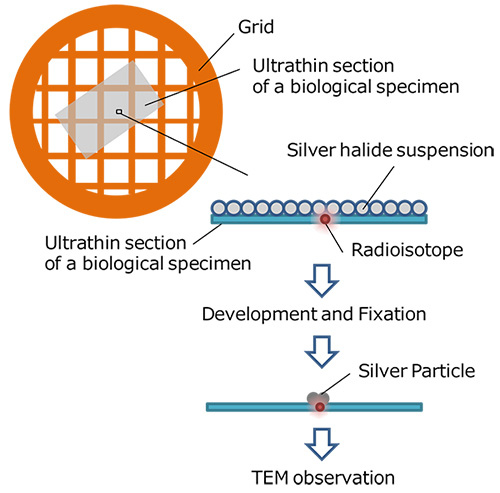
放射性同位元素を含む物質を生体試料に投与し、生体の特定の組織や細胞を標識する。それを超薄切片にし、感光乳剤を塗布する。放射性同位元素が発する放射線(β線)により、標識された部位の近傍の感光乳剤が感光する。これを現像すると、標識された部位に銀が偏析する。この試料を透過電子顕微鏡で観察すると、銀の局在位置から、標識された組織や細胞の位置を特定することができる。
高い分解能で観察するために、感光乳剤の銀を微細に局在偏析させることができる(β線エネルギーの小さい)トリチウムを放射性同位元素として使用することが多い。
例として、放射性トリチウムを含むチミジンを生体に投与して細胞分裂が盛んな部位を標識し、偏析した銀の位置から標識した部位を特定できる。
⇒図
Autoradiography in Electron Microscopy is a method to observe a specific site of a biological specimen labeled with a substance containing a radioactive isotope. The method is implemented in the following procedure.
A substance containing a radioactive isotope is doped into a biological specimen for labeling specific tissues or cells. The biological specimen is thinned down to an ultrathin section and a photo-sensitive emulsion (silver halide suspension) is applied to the thin section. Silver halides in the vicinity of the labeled sites are exposed with β rays emitted from the radioactive isotope. When photo-developed, silver particles are segregated at the labeled sites. When the section is observed with a transmission electron microscope, the positions of the labeled tissues or cells can be identified from the localized silver particles.
In order to perform high-resolution observation of the sites of the labeled tissues or cells, tritium (which emits small energy β-rays) is often used as a radioactive isotope because tritium causes small silver segregates in the photosensitive emulsion.
An example of Autoradiography in Electron Microscopy: Thymidine containing radioactive tritium is applied to label the sites where cell divisions are active in a biological specimen. The labeled sites are revealed from the segregated silver particles by observing the electron microscope image of the specimen.
関連用語から探す
説明に「オートラジオグラフィー」が含まれている用語






