アウトレンズ形対物レンズ
アウトレンズ形対物レンズ
out-lens objective lens, conventional objective lens
[目次:装置]
SEMの誕生以来、最も多く使われてきた対物レンズ。光軸に対して軸対称なレンズである。図に示すように、ヨークの開口部に集中して磁場が作られる(黄色で示した)。試料は、通常レンズの下方10mm程度、あるいはそれ以上離れた位置に置かれるので、レンズと試料の間の距離(作動距離)が長くとれる。その結果、半導体ウェハのような大きな試料を大きく傾斜して観察することができる。さらに、EDSやWDSなどのX線分光器やEBSDなどの検出器を挿入したり、加熱、引っ張り、凍結などの様々なステージを組み込むことができる。試料はレンズ磁場の影響を全く受けないので、磁性材料の観察や分析もできる。ただし、レンズと試料間の距離が長いため、レンズの励磁が弱く収差を小さくできないため、試料上でのプローブサイズを小さくできないので、高分解能観察には不向きである。
アウトレンズ型対物レンズ⇒図
The out-lens objective lens is a most widely used objective lens since the advent of SEM, which is rotationally symmetric with respect to the optical axis of an electron beam. As shown in Figure, A magnetic field is created concentrating at the opening of the yoke (indicated by yellow region).
Since a specimen is placed at a position about 10 mm below the lens or more, a large working distance is created. Thus a large specimen like a semiconductor wafer can be observed at large tilt angles. And an X-ray spectrometer (EDS, WDS), an EBSD detector, or a various-type of stage for heating, stretching or cooling can be installed. Magnetic materials can be observed and analyzed without the magnetic field of the lens. However, since the lens excitation is weak due to the long working distance, the probe size on the specimen is relatively large because lens aberration is not small. Thus, the objective lens is not suitable for high-resolution observation.
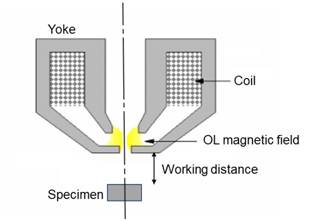
Fig. Schematic of the out-lens objective lens
関連用語から探す
説明に「アウトレンズ形対物レンズ」が含まれている用語






