磁場レンズ
磁場レンズ
magnetic field lens
[目次:装置]
通常SEMに用いられる磁場レンズは、電子ビームを収束させるためのレンズ(凸レンズ)で、光軸に対して回転対称の磁場を利用したものである。SEMの収束レンズや対物レンズに用いられている。
図に回転対称の磁場レンズの断面を模式的に示す。コイルに直流の電流を流して作られた磁場を、透磁率の高い材料(軟鉄)でできた枠(ヨーク)に閉じ込め、ヨークの一部に狭い隙間を作って磁場を局所に集中的に漏洩させて、回転対称な磁場を作る。狭い隙間の先端部分はポールピースと呼ばれ、ヨークに比べて高品質の材料を使い、高い精度で加工されている。
回転対称の磁場レンズの断面例⇒図
The magnetic field lens generally used in SEM is a convex lens to converge an electron beam, which utilizes a magnetic field rotationally-symmetric with respect to the optical axis of the beam. This lens is used as the condenser lens and the objective lens of SEM.
Figure schematically shows the vertical cross section of a rotationally-symmetric magnetic field lens. The magnetic field, which is generated by applying a direct electric current to a magnetic excitation coil, is confined within a yoke composed of a soft iron material with a high permeability. Then, a narrow gap is created in a part of the yoke so that the magnetic field is leaked locally and focused to form a rotationally-symmetric magnetic field. The tip portion of the narrow gap or the magnetic poles is called the pole piece. It is made of a high quality material with a high accuracy processing compared to the yoke.
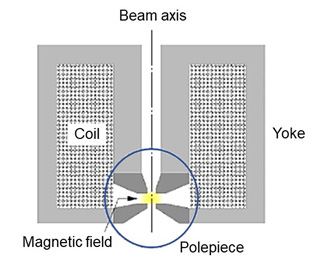
Fig. Example of the vertical cross section of a rotationally-symmetric magnetic lens.
関連用語から探す
説明に「磁場レンズ」が含まれている用語






