低真空SEM
低真空SEM
low-vacuum SEM, Natural SEM, Wet SEM, variable pressure SEM, VP-SEM, Environmental SEM, ESEM, LV-SEM
[目次:装置]
試料室の圧力を数Paから数100Paまで上げられるようにしたSEM。機種によっては2000~3000Paまで圧力を切り替えられるものもある。Environmental SEM (ESEM)、Natural SEMあるいはVP-SEMといった商品名で呼ばれることもある。
試料室の残留ガス分子が、入射電子や試料から放出された電子と衝突することによって陽イオンになることを利用して、試料の帯電を中和する。非導電性試料を導電物質のコーティングをせずに観察できる。通常のSEMで非導電性試料をコーティング無しで観察するためには加速電圧を1kV程度に下げなければならないが、低真空SEMでは加速電圧を下げる必要はない。加えて、ガス放出が非常に多い試料の観察にも有効である。
対物レンズの下端と試料室の間には小さな穴(オリフィス)があるが、差動排気を行うため、試料室の低真空は対物レンズより上の高い真空度を低下させることはない。 試料室に取り付けられる通常の二次電子検出器では、シンチレータに印加された高電圧が放電する可能性があるため使用できない。そこで、反射電子検出器やガス増幅を用いた特殊な二次電子検出器(ESED:environmental secondary electron detector、GSED: gaseous secondary electron detector)が用いられる。
図(a)に低真空SEMの真空排気システムを示す。図(b)に低真空SEMによる帯電の中和の原理を示す。
(a) 低真空SEMの真空排気系統図⇒図
(二次電子検出器※は低真空状態では使用できない。)
(b) 帯電中和の原理⇒図
試料室の残留ガス分子が入射電子や放出電子と衝突して陽イオンとなり、試料表面の電子に引き寄せられて、試料の帯電を中和する。
The Low vacuum SEM (LV-SEM) is designed to increase the pressure in the specimen chamber between a few Pa and a few 100 Pa (low vacuum range). Some LVSEM instruments can switch the pressure from 2000 Pa to 3000 Pa. LV-SEM is also called Environmental SEM (ESEM), Natural SEM, or VP-SEM (product name).
In an LV-SEM, using the cations which are produced from the residual gas molecules in the specimen chamber by collision with the incident electrons or the electrons emitted from the specimen, electrically negative charging of the specimen surface can be neutralized. This phenomenon allows a non-conductive specimen to be observed without conductive coating while avoiding the influence of charging. In an ordinary SEM, the accelerating voltage has to be lowered to about 1 kV to observe non-conductive specimens without coating. However in the LV-SEM, it is not necessary to lower the acceleration voltage to observe non-conductive specimens. In addition, the LV-SEM is also effective to observe a specimen with a lot of out-gasses.
There is a small hole (orifice) between the bottom of the objective lens and the specimen chamber, but due to the differential pumping system in the LV-SEM the part above the objective lens is safely kept at a high vacuum without the influence of the low vacuum of the specimen chamber.
The ordinary secondary electron detector attached to the specimen chamber cannot be used because it can cause discharge due to a high voltage applied to a scintillator. Thus, a backscattered electron detector or a specialized secondary electron detector adopting a gas amplification system (ESED; environmental secondary electron detector or GSED; gaseous secondary electron detector) is used.
Fig. (a) illustrates the vacuum evacuation system of the LV-SEM. Fig. (b) shows the feature of electric charge neutralization in the LV-SEM.
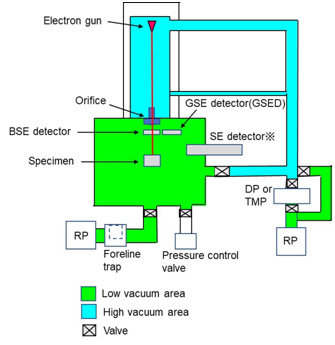
Fig. (a) Schematic of the vacuum evacuation system of an LVSEM.
(The secondary electron detector* cannot be used under a low-vacuum condition.)
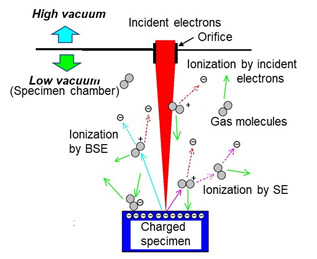
Fig. (b) Feature of charge neutralization.
The residual gas molecules in the specimen chamber become cations by colliding with the incident electrons and the electrons emitted from the specimen. Then, these cations are attracted with the negative charge on the specimen surface. As a result, charging over the specimen surface is neutralized.
関連用語から探す
説明に「低真空SEM」が含まれている用語






