モンテカルロシミュレーション
モンテカルロシミュレーション
Monte Carlo simulation
[目次:理論]
シミュレーション手法の一つで、乱数を利用して確率的に事象をシミュレーションすることの総称。
SEMでは、入射電子が試料中でどのように拡散するかをシミュレーションするために、モンテカルロ法が用いられる。モンテカルロ法のもととなる、固体中の電子の散乱モデルは主に、①弾性散乱にはラザフォード(Rutherford)散乱公式、②非弾性散乱にはベーテ(Bethe)の阻止能(ストッピングパワー)の式が用いられる。これらの理論式に従って、散乱のときに必要な複数のパラメータを乱数を用いて確率的に求め、電子の軌道を順次計算することで、入射電子の拡散の様子をシミュレーションする。求めるパラメータは、弾性散乱による方向変化(散乱角と方位角)、弾性散乱から次ぎの弾性散乱までの距離(自由行程)、非弾性散乱によるエネルギー損失の値である。
このようなシミュレーションを行うソフトウェアは、フリーで公開されたものや商品化されたものがある。これらのソフトウェアでは、試料の元素、試料の層厚(膜厚)、入射電子の数、入射電子のエネルギー、試料への入射角度などが入力されると、各散乱に対して散乱角、自由行程や非弾性散乱によるエネルギー損失の値はソフトウェアによって確率的に与えられ、電子の軌道は自動的に計算され、その条件における入射電子の拡散の様子が表示される。入射電子の拡散のシミュレーションのほかに、X線分光による元素分析のための、特性X線の発生と吸収をシミュレーションするソフトウェアもある。
図は、ソフトウェアを使ってシミュレーションした一例である。10keVの入射電子100個がアルミニウム試料の表面に垂直入射したときの、それらの電子の拡散の様子を示すシミュレーションである。入射電子が0.7~0.8μmの深さまで拡散していることや、入射点から0.5μm程度離れた部位でも後方散乱された電子が試料の表面から放出されることが分かる。
モンテカルロシミュレーションの例⇒図
試料Al、入射電子100個、加速電圧10kV。
Monte Carlo simulation is a computational algorithm in which events are stochastically simulated using the process of repeated random sampling.
In the case of SEM, the Monte Carlo method is used to simulate the behaviors of diffusion of the incident electrons in a specimen. The simulations are performed on the basis of 1) Rutherford scattering formula for elastic scattering and 2) Bethe’s stopping power formula for inelastic scattering in the specimen. According to these formulas, the electron trajectories are calculated one by one where multiple parameters needed at scattering events are stochastically obtained using the random numbers, and the diffusion behaviors of the incident electrons are simulated. Here, the parameters to be used are the scattering angle and azimuth angle of elastic scattering of the incident electrons, the free path length of the electrons (the distance from one scattering to the next scattering), and the value of energy loss due to inelastic scattering.
Commercial and free software programs are available for Monte Carlo simulations. Using those programs, when one inputs the parameters, such as the constituent elements and the layer (film) thickness, the number of the incident electrons, the incident electron energy, the incidence angle onto the specimen, the software stochastically provides the scattering angle, the electron free path and the energy loss value due to inelastic scattering for a scattering event, and then electron trajectories are automatically calculated and the diffusion behaviors of the incident electrons in the specimen are simulated. In addition to the simulation of the diffusion of the incident electrons, the software programs are available which can simulate the generation and absorption of characteristic X-rays in a specimen for elemental analysis by X-ray spectroscopy.
Figure illustrates a simulation example using a software program. This Monte Carlo simulation shows the diffusion behaviors of the incident electrons normal to the surface of an aluminum specimen where the number of the electrons is 100, the accelerating voltage is 10 keV and a specimen thickness of 1μm. It is seen that the incident electrons are diffused into a depth of 0.7 to 0.8 μm from the surface, and that the backscattered electrons generated at a region distant about 0.5 μm from the incident electron beam point are emitted from the upper surface.
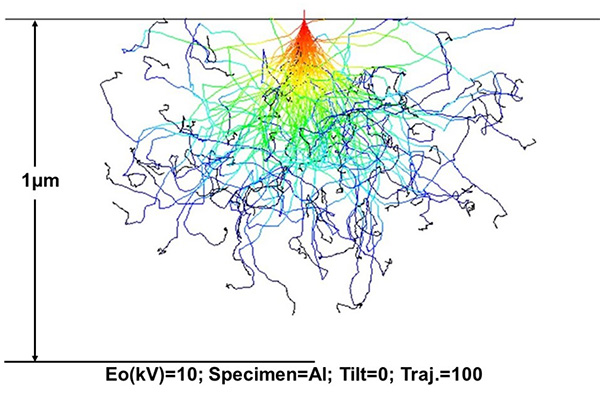
Fig. Example of a Monte Carlo simulation.
1) Specimen: Al 2) The number of incident electrons: 100 3) Accelerating voltage: 10 kV
関連用語から探す
説明に「モンテカルロシミュレーション」が含まれている用語






