グリッド
グリッド
grid
[目次:試料等(試料および試料作製)]
透過電子顕微鏡で観察する試料を載せる直径3 mm、厚さ20~50 μmの金属等の板のこと。四角、丸、スリットなどさまざまな形状を持つグリッドがあり、観察目的に応じて適切な形状のものを選択する。グリッドの材質には銅、モリブデン、金、チタンなどがある。元素分析をする場合は、検出目的の元素を含まない材質のグリッドを使用する。
- 格子状のグリッド
通常使われるグリッド。切片試料や粉砕試料を直接グリッドに載せて観察する。ウイルスや微粒子などの場合は、グリッドの表面に支持膜を張りその上に試料を載せて観察する。 - 単孔グリッド
薄片化した試料片を貼り付けて観察する。格子によって視野が遮られないので、極低倍率の観察に適している。 - 文字(マーク)入りグリッド
観察位置を記憶するマークがグリッド上に付いているため、再度、同じ視野を観察するときに便利である。 - FIB用グリッド
FIBで試料作製した試料片を先端部に付けて観察する。
grid⇒図
A "grid" is a plate of a metal, etc. with a diameter of 3 mm and a thickness of 20 to 50 μm, which supports a specimen for TEM observation. Various grids such as a square-, a circular-, and a slit-grid, are available. They are selectable depending on observation requirements. The material of the grid is copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), gold (Au) or titanium (Ti), etc. In elemental analysis, a grid which does not contain the elements to be analyzed, is used.
- Reticular grid
The grid is most commonly used. Fragmented specimens are placed or pasted on the grid. For viruses or small particles, a supporting film is pasted on the grid and then, the specimen is placed on it. - Single hole grid
The grid is used to observe a wide area of specimen without disturbance of the mesh of a reticular grid. Thus, it is suitable for observation at ultra-low magnifications. - Reference grid
The grid is conveniently used at repeated observation of the same field because the marks (letters) to memorize the observation position are prepared on the grid. - FIB grid
The grid is used to attach a thin film specimen prepared by FIB, to the heads of the grid.
Examples of grid
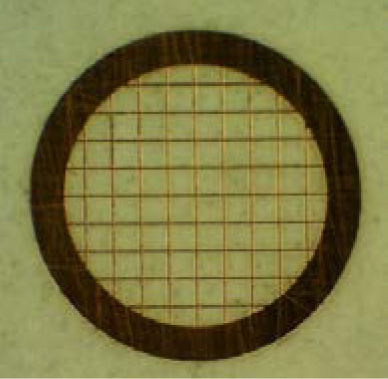
1. Square grid

2. Single hole grid
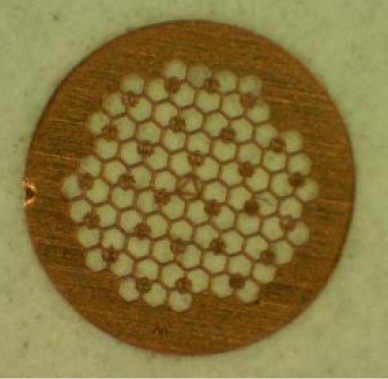
3. Reference grid

4. FIB grid
関連用語から探す
説明に「グリッド」が含まれている用語






