原子散乱因子
原子散乱因子
atomic scattering factor
[目次:理論(電子の散乱/回折/結像)]
入射電子に対する原子1個による散乱振幅のこと。結晶からの回折強度を求めるときに必要な結晶構造因子を計算するために使われる。入射電子は、原子を構成する原子核と電子が作る電場のポテンシャルによって散乱される。散乱振幅は原子番号と共に増加し*、散乱角の増加と共に単調に減少する(図1)。電子線に対する原子散乱因子の単位は[電位]x[体積]である。散乱振幅の角度依存性は、全ての原子について求められており、数値として与えられている(文献1)。また関数による表現もある。
入射電子に対する原子散乱因子の散乱角ゼロでの値は、中性原子に対しては全電位となり有限に留まる。イオン化した原子に対しては散乱角が小さくなると、原子散乱因子は急激に大きくなるので、電子線による散乱(回折)強度はイオン化に対して敏感に変化する。
なお、入射線が X 線の場合には、電子のみによって散乱され、中性原子に対しては原子散乱因子の散乱角ゼロでの値は原子の電子数 Z になる。X 線に対する原子散乱因子の単位は無次元である。
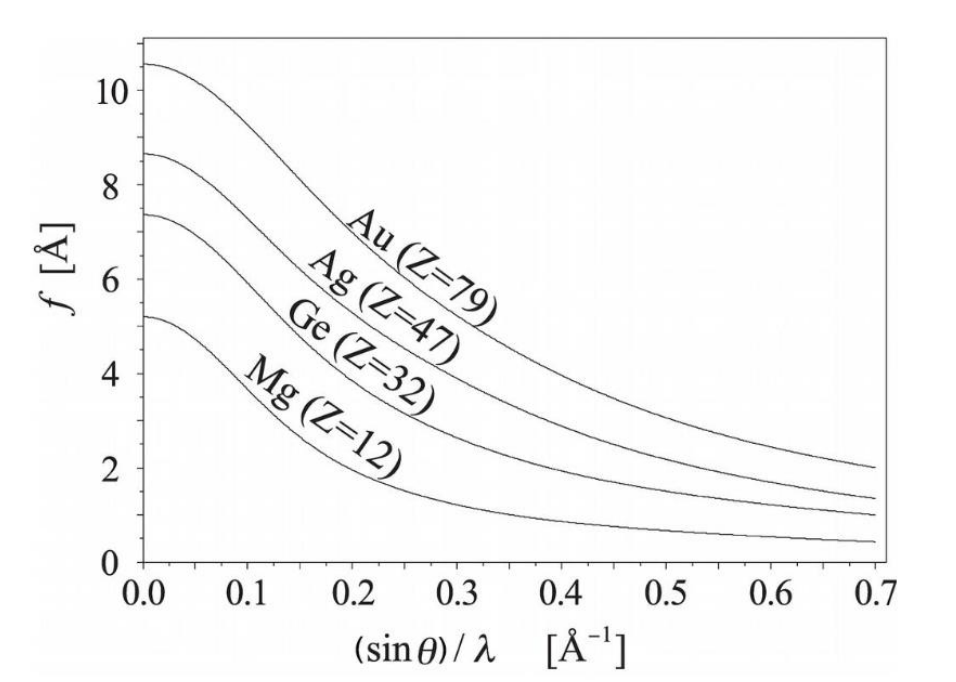
図 1:入射電子に対する原子散乱因子の散乱角(sinθ/λ)依存性[文献 1]*:軽元素の場合には散乱角が小さい領域では散乱振幅が原子番号の順にならないことがある。
文献 1: International Tables for Crystallography (2006). Vol. C. ch. 4.3, pp. 259-429
https://doi.org/10.1107/97809553602060000593
The atomic scattering factor is the scattering amplitude by an atom for an incident electron. This factor is used to calculate the crystal structure factor, which is needed to obtain the diffraction intensity from a crystal.
An incident electron is scattered by the electrostatic potential created by an atomic nucleus and surrounding electrons. The scattering amplitude increases with increasing the atomic number* and monotonically decreases with increasing the scattering angle (Fig. 1). The unit of the atomic scattering factor for an incident electron is [Potential] x [Volume]. The angular dependence of the scattering amplitude has been obtained for all the elements and is given with the numerical values (Ref.1). Expressions of the scattering amplitudes using a mathematical function are also available. The value of the atomic scattering factor at zero angle scattering for the incident electron beam is the total electrostatic potential (value), which is finite, for the neutral atom. For an ionized atom, the atomic scattering factor rapidly increases with decreasing the scattering angle. This means that the scattering (diffraction) intensity of the electron beam changes sensitively against ionization.
It is noted that, when the incident beam is an X-ray, it is scattered only by electrons, and that the value of the atomic scattering factor for a neutral atom at zero scattering angle is the number of electrons of the atom Z. Thus, the units of the atomic scattering factors for X-rays are dimensionless.

Fig. 1. Scattering angle dependence (sinθ/λ) of the four atomic scattering factors for an incident electron. (Ref. 1) *: For light elements, the scattering amplitudes are not always in the order of atomic number in the regions where the scattering angle is small.
Ref.1: International Tables for Crystallography (2006). Vol. C. ch. 4.3, pp. 259-429
https://doi.org/10.1107/97809553602060000593
関連用語から探す
説明に「原子散乱因子」が含まれている用語






