ゼルニケ位相コントラスト
ゼルニケ位相コントラスト
Zernike phase contrast
[目次:理論(電子の散乱/回折/結像)]
透過電子顕微鏡で、位相物体の観察に位相板あるいはレンズの球面収差と焦点はずしの効果を利用し、試料によって散乱された電子波の位相変化を振幅の変化に変換することによって得られるコントラスト。
Zernike phase contrast⇒図1
(a) Conventional TEM (C-TEM) 像 (b) Zernike phase contrast (ZPC-TEM) 像。加速電圧:200kV。試料:氷包埋された T4 ファージ。 (c) T4 ファージの模式図。
ZPC-TEM 像では、C-TEM像に比べて、カプシド(Capsid)内部のDNAの微細構造、カプシド表面にある毛状構造物、筒状構造等が、より高いコントラストで観察されている。
In TEM, "Zernike phase contrast" means contrast which is obtained by converting the phase change of electron waves scattered by a specimen into the amplitude change. The conversion is performed by using a phase plate or a combined effect of the spherical aberration of the electron lens and defocus.
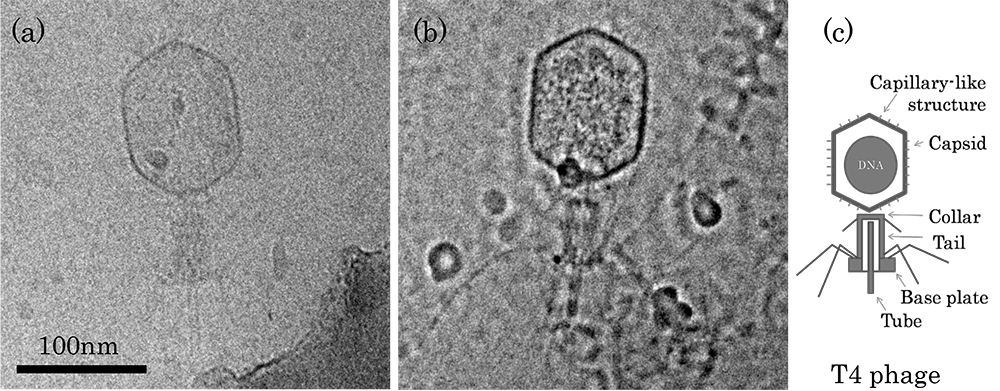
(a) Conventional TEM (C-TEM) image.
(b) Zernike phase contrast (ZPC-TEM) image of an ice-embedded T4 phage taken at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV.
(c) Schematic of T4 phage.
Compared with the C-TEM image, the ZPC-TEM image clearly visualizes the fine structures of DNA in a capsid, the hair-like structural objects and the cylindrical structures on the capsid surface.
関連用語から探す
説明に「ゼルニケ位相コントラスト」が含まれている用語






