仮想光源
仮想光源
virtual source
[目次:装置]
電界放出型電子銃およびショットキー電子銃の見かけ上の光源を仮想光源といい、実際上、光源として扱われる。
電界放出型電子銃のタングステンの電子源(エミッター)の先端の曲率半径は100~200nmである。ここに数キロボルトの引き出し電圧によって強い電界がかけられると、電子はエミッターから放出される。図1に示すように、この表面から放出された電子は、あたかもエミッター内部の直径5~10nmの光源から放出されたような軌道をとる。この光源のことを仮想光源という。図2に示すように、放出された電子は、陽極に掛けられた電圧によって所定の電圧まで加速される。
電界放出電子銃の輝度が高いのは、この光源(仮想光源)が極めて小さいことによる。ショットキー電子銃の仮想光源は電界放出型電子銃に比べると、若干大きく15~20nmである。
仮想光源の概念⇒図1
電界放出電子銃の構造⇒図2
The virtual source is the real electron source of the field-emission electron gun (FEG) and the Schottky-emission electron gun.
The radius of the curvature of the tip of the tungsten (W) emitter for FEG is 100 to 200 nm. A strong electric field is applied to the tip by an extraction voltage, and then the electrons are emitted from the surface of tip. As shown in Fig.1, the electron beam behaves as if it emanates from a source of 5 to 10 nm diameter. This source is called the virtual source. As shown in Fig.2, the emitted electrons are accelerated up to a designated voltage by the voltage applied to the anode.
The high brightness of FEG results from the extremely small virtual source. The virtual source of the Schottky-emission electron gun is a little larger than that of FEG, 15 to 20 nm in diameter.
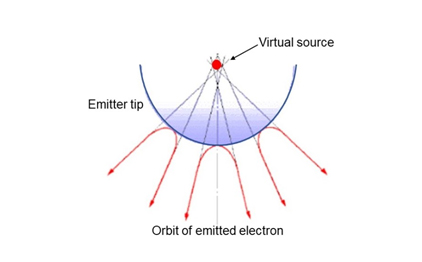
Fig. 1 Conceptual diagram of the virtual source
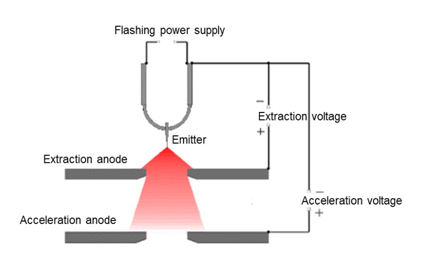
Fig. 2 Structure of FEG
関連用語から探す
説明に「仮想光源」が含まれている用語






